The Notre Dame Integrated Imaging Facility (NDIIF) is pleased to announce two awards for best imaging publications for the 2014 calendar year.
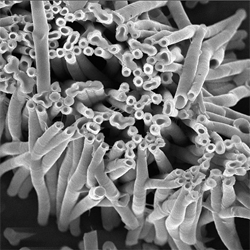
The Best Electron Microscopy Imaging Publication 2014 is awarded to Rajesh Sahadevan, a post-doctoral research associate with Professor W. A. Philip in in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. Sahadevan and coworkers published a paper titled “Mixed Mosaic Membranes Prepared by LayerbyLayer Assembly for Ionic Separations”. The project addressed the fabrication of mixed mosaic membranes (MMMs) with discrete positively charged and negatively charged domains. Due to this unique nanostructure, MMMs are capable of selectively separating dissolved ions from similarly-sized neutral solutes.
Using the Magellan 400 scanning electron microscope (SEM) located in Stinson Remick Hall, micrographs were acquired that illustrated the feasibility of a layer-by-layer (LbL) technique to fabricate these unique membranes. Furthermore, SEM micrographs of the polymeric nanotubes helped control the dimensions (i.e., length, inner diameter and outer diameter) of these building blocks. The study was published in ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 12338–12345, DOI: 10.1021/nn504736w.
View Rajesh Sahadevan’s mosaic micrographs (PDF).
The Best Biological Imaging Publication 2014 is awarded to Lisa Cole, a graduate student with Professor R. K. Roeder in the Bioengineering Graduate Program, Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, and a collaborator with Professor T. Vargo-Gogola in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Indiana University School of Medicine-South Bend. Cole and coworkers published a paper titled, “Contrast-Enhanced X-ray Detection of Breast Microcalcifications in a Murine Model Using Targeted Gold Nanoparticles”.
Mammography is a clinical X-ray imaging tool for the early detection of breast cancer and the paper focused on microcalcifications of hydroxyapatite mineral within breast tissue and the most common abnormality detected by mammography. The detection of microcalcifications is limited by the sensitivity and specificity of mammography. The study investigated targeted delivery of bisphosphonate-functionalized gold nanoparticles for contrast-enhanced detection of microcalcifications using computed tomography. A combination of X-ray CT and TEM imaging data demonstrated for the first time that a targeted X-ray contrast agent could be used to improve the sensitivity and specificity of X-ray imaging for the early detection of breast microcalcifications. The study was published in ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 7486-7496, DOI: 10.1021/nn5027802.
View Lisa Cole’s images (PDF)
Originally published by at science.nd.edu on April 23, 2015.